Debt-To-Equity Ratio: Explanation, Formula, Example Calculations
In such industries, a high debt to equity ratio is not a cause for concern. There are several metrics that are used to gauge the financial health of a company, how the company finances its business operations and assets, as well as its level of exposure to risk. These balance sheet categories may include items that would not normally be considered debt or equity in the traditional sense of a loan or an asset. Because the ratio can be distorted by retained earnings or losses, intangible assets, and pension plan adjustments, further research is usually needed to understand to what extent a company relies on debt. A low debt to equity ratio means a company is in a better position to meet its current financial obligations, even in the event of a decline in business.
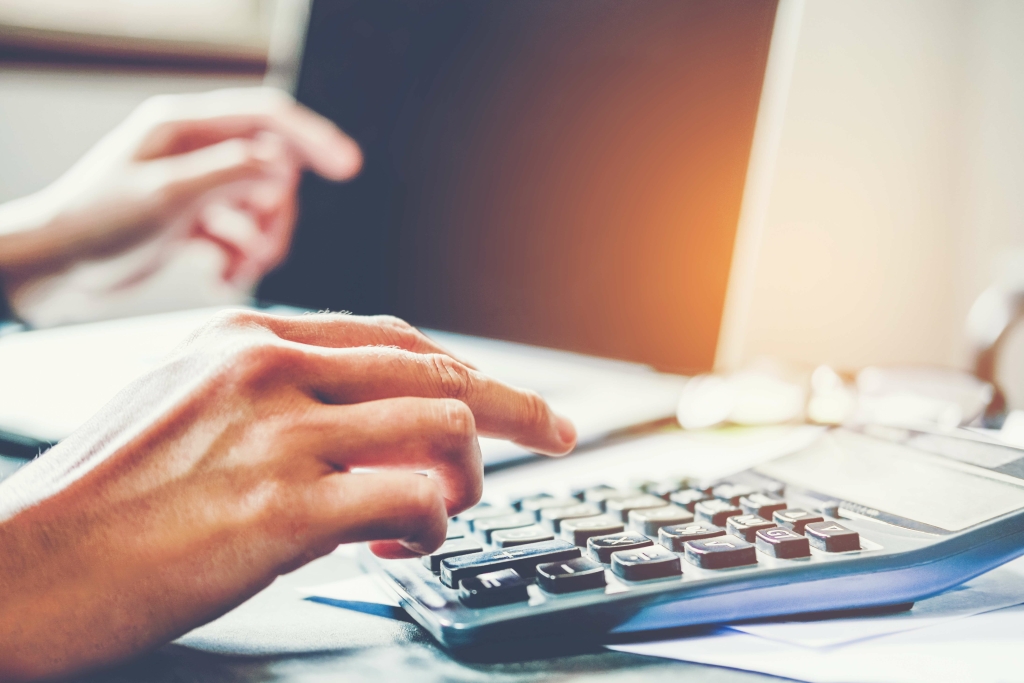
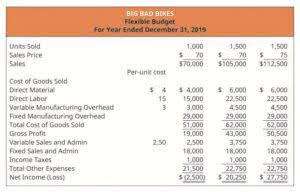
While a useful metric, there are a few limitations of the debt-to-equity ratio. As you can see from the above example, it’s difficult to determine whether a D/E ratio is “good” without looking at it in context. This means that for every dollar in equity, the firm has 76 cents in debt. The following D/E ratio calculation is for Restoration Hardware (RH) and is based on its 10-K filing for the financial year ending on January 29, 2022.
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
They also assess the D/E ratio in the context of short-term leverage ratios, profitability, and growth expectations. In other industries, such as IT, which don’t require much capital, a high debt to equity ratio is a sign of great risk, and therefore, a much lower debt to equity how do i create a new category or subcategory ratio is more preferable. If a bank is deciding to give this company a loan, it will see this high D/E ratio and will only offer debt with a higher interest rate in order to be compensated for the risk. The interest payments will be higher on this new round of debt and may get to the point where the business isn’t making enough profit to cover its interest payments.
To illustrate, suppose the company had assets of $2 million and liabilities of $1.2 million. Because equity is equal to assets minus liabilities, the company’s equity would be $800,000. Its D/E ratio would therefore be $1.2 million divided by $800,000, or 1.5.
Additional Resources
For this to happen, however, the cost of debt should be significantly less than the increase in earnings brought about by leverage. The bank will see it as having less risk and therefore will issue the loan with a cash payment journal lower interest rate. This company can then take advantage of its low D/E ratio and get a better rate than if it had a high D/E ratio. But, if debt gets too high, then the interest payments can be a severe burden on a company’s bottom line.
Overall, the D/E ratio provides insights highly useful to investors, but it’s important to look at the full picture when considering investment opportunities. The nature of the baking business is to take customer deposits, which are liabilities, on the company’s balance sheet. They do so because they consider this kind of debt to be riskier than short-term debt, which must be repaid in one year or less and is often less expensive than long-term debt.
That is, total assets must equal liabilities + shareholders’ equity since everything that the firm owns must be purchased by either debt or equity. The current ratio measures the capacity of a company to pay its short-term obligations in a year or less. Analysts and investors compare the current assets of a company to its current liabilities.
Whereas, equity financing would entail the issuance of new shares to raise capital which dilutes the ownership stake of existing shareholders. Debt financing is often seen as less risky than equity financing because the company does not have to give up any ownership stake. There are various companies that rely on debt financing to grow their business. For example, Nubank was backed by Berkshire Hathaway with a $650 million loan. A low D/E ratio shows a lower amount of financing by debt from lenders compared to the funding by equity from shareholders. For purposes of simplicity, the liabilities on our balance sheet are only short-term and long-term debt.
However, if the company were to use debt financing, it could take out a loan for $1,000 at an interest rate of 5%. Below is a short video tutorial that explains how leverage impacts a company and how to calculate the debt/equity ratio with an example. In the example below, we see how using more debt (increasing the debt-equity ratio) increases the company’s return on equity (ROE). By using debt instead of equity, the equity account is smaller and therefore, return on equity is higher. So, the debt-to-equity ratio of 2.0x indicates that our hypothetical company is financed with $2.00 of debt for each $1.00 of equity. The D/E ratio represents the proportion of financing that came from creditors (debt) versus shareholders (equity).
If a company takes out a loan for $100,000, then we would expect its D/E ratio to increase. Our company now has $500,000 in liabilities and still has $600,000 in shareholders’ equity. Total assets have increased to $1,100,000 due to the additional cash received from the loan.
Why are D/E ratios so high in the banking sector?
- From the above, we can calculate our company’s current assets as $195m and total assets as $295m in the first year of the forecast – and on the other side, $120m in total debt in the same period.
- It is the opposite of equity financing, which is another way to raise money and involves issuing stock in a public offering.
- The investor has not accounted for the fact that the utility company receives a consistent and durable stream of income, so is likely able to afford its debt.
- For purposes of simplicity, the liabilities on our balance sheet are only short-term and long-term debt.
This could lead to financial difficulties if the company’s earnings start to decline especially because it has less equity to cushion the blow. A good D/E ratio of one industry may be a bad ratio in another and vice versa. Another example is Wayflyer, an Irish-based fintech, which was financed with $300 million by J.P. Upon plugging those figures into our formula, the implied D/E ratio is 2.0x. At first glance, this may seem good — after all, the company does not need to worry about paying creditors. The D/E ratio is much more meaningful when examined in context alongside other factors.
These are excluded from the D/E ratio because they are not liabilities due to financing activities and are typically short term. The D/E ratio does not account for inflation, or moreover, inflation does not affect this equation. A company with a D/E ratio greater than 1 means that liabilities are greater than shareholders’ equity. A D/E ratio less than 1 means that shareholders’ equity is greater than total liabilities. A Debt to Equity Ratio greater than 1 indicates that a company has more debt than equity.
Is there any other context you can provide?
This usually signifies that a company is in good financial health and is generating enough cash flow to cover its debts. The debt-to-equity ratio (D/E) compares the total debt balance on a company’s balance sheet to the value of its total shareholders’ equity. The debt-to-equity (D/E) ratio can help investors identify highly leveraged companies that may pose risks during business downturns. Investors can compare a company’s D/E ratio with the average for its industry and those of competitors to gain a sense of a company’s reliance on debt. Debt-financed growth may serve to increase earnings, and if the incremental profit increase exceeds the related rise in debt service costs, then shareholders should expect to benefit. However, if the additional cost of debt financing outweighs the additional income that it generates, then the share price may drop.
This in turn makes the company more attractive to investors and lenders, making it easier for the company to raise money when needed. However, a debt to equity ratio that is too low shows that the company is not taking advantage of debt, which means it is limiting its growth. A company’s debt to equity ratio provides investors with an easy way to gauge the company’s financial health and its capital infrastructure. The simple formula for calculating debt to equity ratio is to divide a company’s total liabilities by its total equity.